An ICCT report by Bryan Comer, Naya Olmer, Xiaoli Mao, Biswajoy Roy, and Dan Rutherford
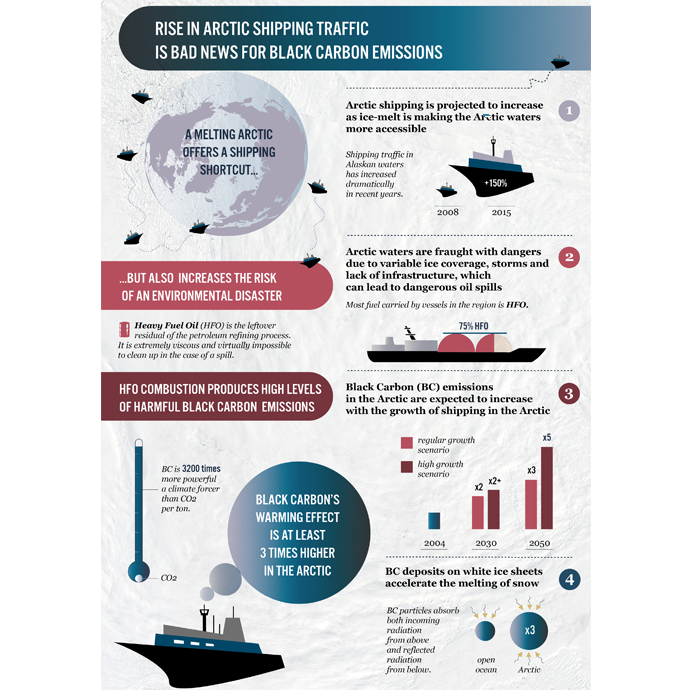
Ships are an efficient way to move cargo, transporting approximately 80% of the world’s goods by volume, but ships also threaten human health, ecosystems, and the climate. This report focuses on the air and climate pollutant black carbon (BC). This report presents a bottom-up, activity-based global inventory of BC emissions, residual fuel use, and residual fuel carriage from commercial ships in the global fleet for the year 2015. In addition, the report analyzes the BC reduction potential of four technology scenarios: switching all ships from residual to distillate fuels; switching some ships from residual or distillate fuel to LNG; installing exhaust gas cleaning systems on ships; and installing diesel particulate filters (DPFs).